Doutorando: Huarlen Marcio Balbino. Data: 26/05/2020, às 16:00 horas pelo canal do YouTube (pos.fitopatologia UFV) Link: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCCZZh5mUepI3YHAYxBuU7qw. Orientador: Leandro Grassi de Freitas
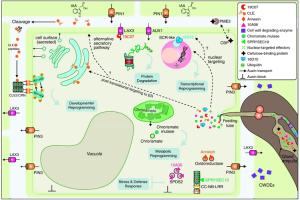
Plant parasitic nematodes are microscopic worms that have the ability to infect plant roots, causing great losses to agriculture. For the success of parasitism, these vegetable parasites secrete a cocktail of proteins and effector molecules that are capable of causing continuous morphological and physiological changes in the host. Nematode effectors can assist in the penetration and migration in the plant tissues, suppress immune responses of the host defense and, for the sedentary endoparasitic nematodes, assist in the development of specialized structures to obtain nutrients. The search for peptides with signal for secretion and without transmembrane domain, and the use of in situ hybridization techniques, interference RNA and subcellular localization contributed to the identification and understanding of how nematode effectors manipulate their hosts. Most works of identification and functional characterization of effectors are focused on nematodes of the genus Meloidogyne, Heterodera